Featured Resources

Change Orders, Productivity, Overtime—A Primer for the Construction Industry
This planning tool helps you determine the costs associated with unplanned events, circumstances and factors that may impact the outcome, productivity and schedule of construction projects. New for 2024: a chapter exploring the factors that contribute to BIM cost and time overruns.
Mental Health Awareness & Suicide Prevention Video
Our newest safety and health video highlights the success story of an industry veteran, with appearances from MCAA’s president Robert Beck, the UA’s Jen Massey, industry expert Dr. Sally Spencer Thomas, and MCAA member Ricky Reams.
WebLEM is the industry’s most reliable authority for comprehensive labor units for typical project tasks. Quickly search for and retrieve information. WebLEM is reviewed and updated to reflect the latest products and joining methods. You will need your MCAA.org username and password to log in to WebLEM. For WebLEM access questions, please refer to the WebLEM Access FAQs page.

National Service and Maintenance Agreement
The National Service and Maintenance Agreement is an agreement negotiated and administered by the United Association of Journeymen and Apprentices of the Plumbing and Pipefitting Industry (UA) and the Mechanical Service Contractors of America (MSCA) and is a signed contract between the UA and individual mechanical service contracting firms who apply and qualify. The Agreement is a nationally recognized tool that helps contractors provide quality, consistent service to their customers throughout the country and helps reclaim lost market share.

MCAA CEO Tim Brink has been honored with the Albert Nelson Marquis Lifetime Achievement Award from Marquis Who’s Who®, the leading publisher of biographical profiles. This prestigious award recognizes Tim’s outstanding leadership, achievements, and significant contributions to the mechanical and plumbing industry.
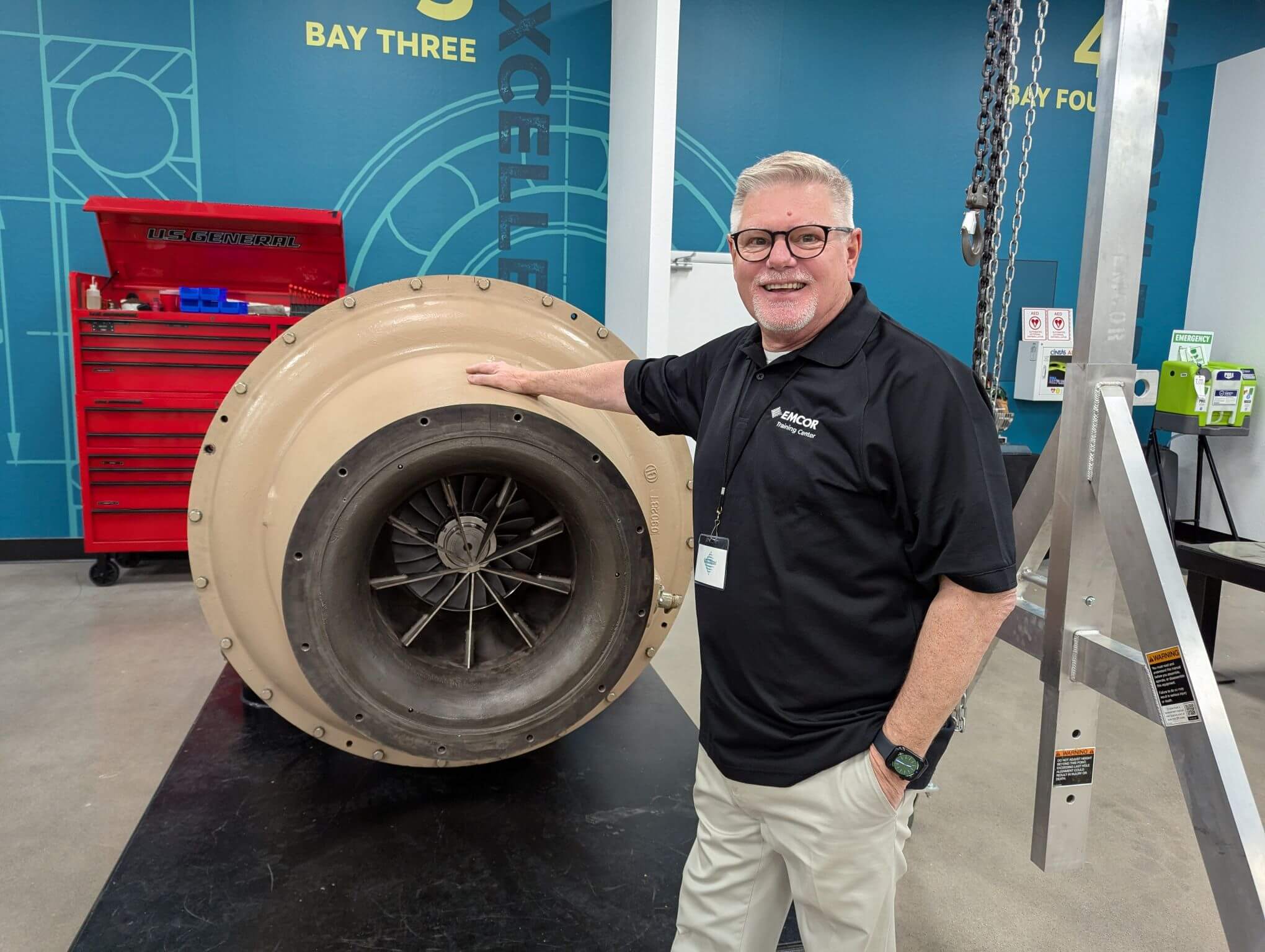
EMCOR Services, an MCAA and MSCA member, recently opened a new, 11,000-square-foot, state-of-the-art training facility in Phoenix, AZ. The facility lets EMCOR employees from across the nation attend in-person training sessions on topics ranging from the latest OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) equipment to safety best practices to automation-line tutorials, and everything in between—all while gaining valuable insights gleaned from real-life work situations. A collaboration between MSCA and the new EMCOR Training Center gives members access to MSCA classes at the facility.
The NCPWB Technical Conference is just around the corner! Don’t miss this exciting opportunity to learn, share, and connect. This year’s conference is packed with valuable content and unmatched opportunities to network with friends, colleagues, and new acquaintances. We’re also introducing for the first time, an exhibitor showcase on Monday afternoon where you can see the latest and greatest welding technologies. Don’t miss it – register today!
The Manufacturer/Supplier Training area of MCAA’s website connects our contractor members with training opportunities available from the members of MCAA’s Manufacturer/Supplier Council.
If you enjoyed the PCA Lunch and Learn at Convention, and its lively discussion on plumbing special projects, get ready to take your plumbing service knowledge to the next level at the PCA Plumbing Service Conference! This event is your best opportunity to learn, share, and grow in your understanding of plumbing service operations. Whether you’re looking to refine your strategies, gain insights from industry leaders, or connect with peers who share your challenges and opportunities, this conference is designed with you in mind. Register today and be part of the future of plumbing service!
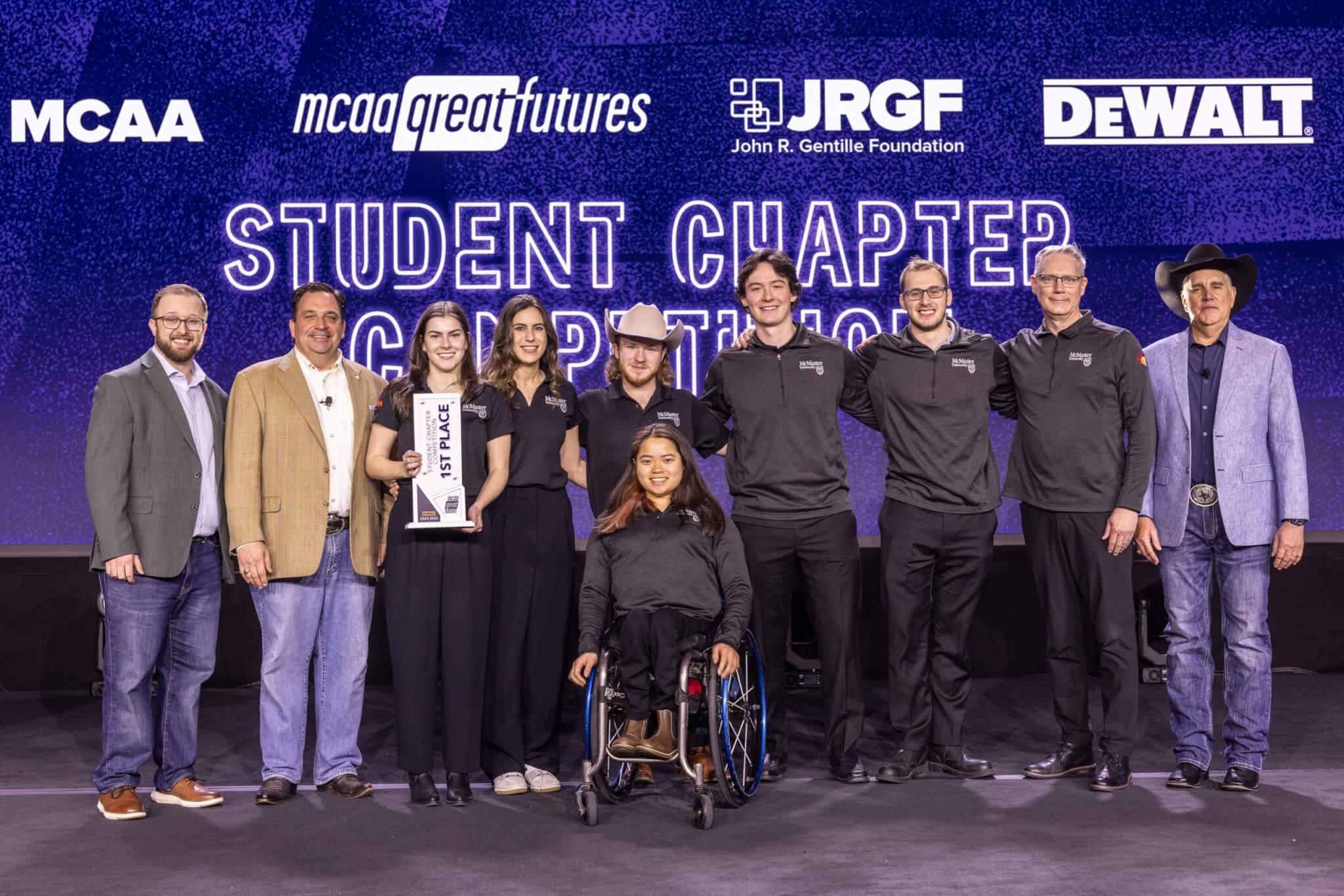
Twenty-three students were recognized with a variety of scholarships and for the first time, the scholarship total reached $100,000! McMaster University emerged as the victors for the Student Chapter Competition and returned to campus with a $10,000 prize, sponsored by DEWALT Industrial Tool Company, following their Final Four presentation at MCAA25. The MVP – Most Valuable Presenter was awarded to Parker Jenkins from Pittsburg State University. Congratulations to all MCAA25 award winners and scholarship recipients!
MCAA’s Virtual Trade Show connects our contractor members with the members of MCAA’s Manufacturer/Supplier Council.
Thomas J. Wanner, retired Executive Director of the MCA/MSCA of Cleveland, Inc. and a past chair of MCAA’s Association Executives Council, passed away on March 7, 2025. He will be sorely missed and fondly remembered by the entire MCAA family.
An analysis of more than 2,500 bids on 773 Illinois Capital Development Board (CDB) building projects between 2017 and 2023 has found that project labor agreements (PLAs) increased bid competition by an average of 14 percent, with each additional bid increasing the likelihood that projects would be awarded below their official engineer’s estimates by 6 percent. The report was published by researchers at the Illinois Economic Policy Institute (ILEPI) and the Project for Middle Class Renewal (PMCR) at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
As a business owner in the mechanical contracting industry, you already juggle enough—projects, workforce management, regulations, and keeping up with an ever-changing market. But what happens in Washington, D.C. directly impacts your bottom line. The CEA National Issues Conference is your chance to influence the policies affecting your business, rather than just reacting to them after they’re set. This is your chance to shape the future of the mechanical contracting industry. Don’t just watch the change—be part of it. Register today!
As part of its ongoing commitment to protecting your livelihood and setting the stage for a bright future, MCAA has secured the services of Longbow Public Policy Group to advise our MCAA Government Affairs Committee (GAC). GAC Chair, Jim Gaffney will be passing along information relative to our industry on a regular basis.
As Women in Construction Week comes to a close, the industry continues to celebrate the invaluable contributions of women who are shaping the future of construction. This week has highlighted their achievements, honored their dedication, and sparked inspiration for future generations to pursue careers in this dynamic field.
MCAA’s web-based labor estimating manual is an invaluable tool for your business. Free as a benefit of your membership.
WebLEM
Scholarships are just one way the John R. Gentille Foundation is investing in your industry’s future. Have you invested in it?
JRGF
You can make an impact on the future of your industry and your business by contributing to the MCAA Political Action Committee.
MCAA PAC
Looking for an intern? You can head to our improved student chapter website and check out the great resumes there!
MCAAGreatFutures
The year-round involvement of our manufacturer/supplier members is part of what makes MCAA special. Learn more about the Council and the value it brings to MCAA.